SUMMARY OF THE PROGRAM
This program is designed to equip you with the knowledge, skills and attitudes that constitute the base for a set of entry-level competencies required to practice as dietician. The dietitian is a highly qualified health professional who is expert in food and nutrition and advises people on what to eat in order to lead a healthy lifestyle or achieve a specific medical goal. Dietitians work in clinical and community settings as well as in food industry.
Legal frame of the program:
Conditions for admission :
Legal frame of the program:
- Number and date of the authorization : 04/01328 - 07/07/2017
- Number and date of the accreditation : 04/01516 – 28/07/201
Conditions for admission :
- High school diploma (Abitur, Baccalaureat, GCE-A Level) in a scientific specialty
- Admission tests
- Computer knowledge
- Good morality
- Physical and mental fitness
DESCRIPTION OF THE PROGRAM

This program is tailored to equip you with the knowledge, skills and attitudes that will make you a competent Dietician.
In this program you will get a solid foundation in biological and medical sciences, which enables you to comprehend human health and diseases and their attributes. The program capitalizes then on this foundation for building up your competencies for practice through learning everything about food and nutrition. You will get to know the composition of food and how the food constituents such as proteins, carbohydrates, fats, minerals and vitamins affect the body at a biochemical level.
You will also understand how these effects can contribute to health and growth of the body or disease and ailment. You will also understand the reciprocal interaction between diet and disease and how diet should be adapted to various pathologies and organ impairments.
The program complements this complex knowledge base with practical competencies of planning and implementing dietetic interventions for patients and healthy individuals in a variety of settings. You will be extensively trained on clinical dietetics encompassing nutritional services for critically-ill patients as well as patients with acute and chronic diseases. You will also master nutritional therapy for patients with weight and eating disorders.
The program will also build your capacity in nutritional counseling. You will be able to educate patients and healthy individuals on how to maintain a healthy life style through balanced diet tailored to individual needs. You will also learn how to manage food services and help institutions provide healthy food and comply with food hygiene standards.
The job outlook after graduation is very bright. The demand for qualified dietitians is very high in Morocco and abroad. Hospitals and other health care facilities are increasingly hiring clinical dietitians than ever before. Increased public interest in nutrition has led to job opportunities in food manufacturing, advertising, and marketing. Qualified dietitians are increasingly required to oversee large-scale meal planning and preparation in healthcare facilities, schools, hotels, hostels, company cafeterias and correction facilities.
We have designed the course in a way that offers you the most interactive, informal and encouraging environment conducive to learning. You will be encouraged to think critically, to seek knowledge yourself and to translate theory into practice. Our curriculum is based on the art and science of helping you learn. The principles of our educational philosophy are that you are a self-directed learner, have rich experiences and knowledge on which to draw and desire to learn to better handle real-life situations. In this regard we see education as a process that builds up competences and leads to achievement of your full potential. Last but not least, every facility that makes you enjoy learning shall be at your disposal.
We are confident that you will excel in this program and wish you all the best.
In this program you will get a solid foundation in biological and medical sciences, which enables you to comprehend human health and diseases and their attributes. The program capitalizes then on this foundation for building up your competencies for practice through learning everything about food and nutrition. You will get to know the composition of food and how the food constituents such as proteins, carbohydrates, fats, minerals and vitamins affect the body at a biochemical level.
You will also understand how these effects can contribute to health and growth of the body or disease and ailment. You will also understand the reciprocal interaction between diet and disease and how diet should be adapted to various pathologies and organ impairments.
The program complements this complex knowledge base with practical competencies of planning and implementing dietetic interventions for patients and healthy individuals in a variety of settings. You will be extensively trained on clinical dietetics encompassing nutritional services for critically-ill patients as well as patients with acute and chronic diseases. You will also master nutritional therapy for patients with weight and eating disorders.
The program will also build your capacity in nutritional counseling. You will be able to educate patients and healthy individuals on how to maintain a healthy life style through balanced diet tailored to individual needs. You will also learn how to manage food services and help institutions provide healthy food and comply with food hygiene standards.
The job outlook after graduation is very bright. The demand for qualified dietitians is very high in Morocco and abroad. Hospitals and other health care facilities are increasingly hiring clinical dietitians than ever before. Increased public interest in nutrition has led to job opportunities in food manufacturing, advertising, and marketing. Qualified dietitians are increasingly required to oversee large-scale meal planning and preparation in healthcare facilities, schools, hotels, hostels, company cafeterias and correction facilities.
We have designed the course in a way that offers you the most interactive, informal and encouraging environment conducive to learning. You will be encouraged to think critically, to seek knowledge yourself and to translate theory into practice. Our curriculum is based on the art and science of helping you learn. The principles of our educational philosophy are that you are a self-directed learner, have rich experiences and knowledge on which to draw and desire to learn to better handle real-life situations. In this regard we see education as a process that builds up competences and leads to achievement of your full potential. Last but not least, every facility that makes you enjoy learning shall be at your disposal.
We are confident that you will excel in this program and wish you all the best.
outcomes of the program

The academic program draws on the PDEP-PFPN integrated framework and intends to build a set of entry-level or threshold competencies organized in seven various professional domains of the dietetics practice.
DOMAIN 1. FOOD AND NUTRITION EXPERTISE:
Dietitians integrate their food and nutrition expertise to support the health of individuals, communities and populations
DOMAIN 2. PROFESSIONALISM AND ETHICS:
Dietitians use professional, ethical and client-centred approaches, to practice with integrity and accountability
DOMAIN 3. COMMUNICATION AND COLLABORATION:
Dietitians communicate effectively and collaborate with others to achieve practice goals
DOMAIN 4. MANAGEMENT AND LEADERSHIP:
Dietitians use management skills and provide leadership to advance health, through food and nutrition
DOMAIN 5. NUTRITION CARE:
Dietitians use the Nutrition Care Process to provide individualized care
DOMAIN 6. POPULATION HEALTH PROMOTION:
Dietitians assess food and nutrition needs with communities / populations, and collaborate in planning to promote health
DOMAIN 7. FOOD PROVISION:
Dietitians manage and consult on quantity food provision to support health
DOMAIN 1. FOOD AND NUTRITION EXPERTISE:
Dietitians integrate their food and nutrition expertise to support the health of individuals, communities and populations
- Apply understanding of food composition and food science
- Apply understanding of food environments
- Apply understanding of human nutrition and metabolism
- Apply understanding of dietary requirements and guidelines
- Apply understanding of dietary practices
- Integrate nutrition care principles and practices
- Integrate population health promotion principles and practices
- Integrate quantity food provision principles and practices
DOMAIN 2. PROFESSIONALISM AND ETHICS:
Dietitians use professional, ethical and client-centred approaches, to practice with integrity and accountability
- Act ethically and with integrity
- Practice in a manner that promotes cultural safety
- Employ a client-centred approach
- Practice according to legislative, regulatory and organizational requirements
- Ensure appropriate and secure documentation
- Use risk management approaches
- Manage time and workload
- Employ an evidence-informed approach to practice
- Engage in reflective practice
- Practice within limits of current personal level of professional knowledge and skills
- Maintain comprehensive and current knowledge relevant to practice
- Use information management technologies to support practice
DOMAIN 3. COMMUNICATION AND COLLABORATION:
Dietitians communicate effectively and collaborate with others to achieve practice goals
- Use appropriate communication approaches
- Use effective written communication skills
- Use effective oral communication skills
- Use effective electronic communication skills
- Use effective interpersonal skills
- Engage in teamwork
- Participate in collaborative practice
DOMAIN 4. MANAGEMENT AND LEADERSHIP:
Dietitians use management skills and provide leadership to advance health, through food and nutrition
- Manage programs and projects
- Assess and enhance approaches to practice
- Participate in practice-based research activities
- Undertake knowledge translation
- Advocate for ongoing improvement of nutritional health and care
- Foster learning in others
- Foster development of food literacy in others
- Foster development of food skills in others
DOMAIN 5. NUTRITION CARE:
Dietitians use the Nutrition Care Process to provide individualized care
- Conduct nutrition assessment
- Determine nutrition diagnosis
- Plan nutrition intervention(s)
- Implement nutrition intervention(s)
- Monitor nutrition intervention(s) and evaluate achievement of nutrition goals
DOMAIN 6. POPULATION HEALTH PROMOTION:
Dietitians assess food and nutrition needs with communities / populations, and collaborate in planning to promote health
- Assess food- and nutrition-related situation of communities and populations
- Determine food- and nutrition-related issues of communities and populations
- Develop food- and nutrition-related community / population health plan
- Implement food- and nutrition-related community / population health plan
- Monitor and evaluate food- and nutrition-related community / population health plan
DOMAIN 7. FOOD PROVISION:
Dietitians manage and consult on quantity food provision to support health
- Determine food provision requirements of a group / organization
- Plan food provision
- Manage food provision
- Monitor and evaluate food provision
International equivalence |
The academic program is organized over three years (six semesters). Successful completion of this program requires:
Students receive credits for their class time and for their work outside of class. The schedule for this program encompasses:
The American equivalence is based on the Carnegie system. A semi-annual Carnegie loan is worth 45 hours. For a clinical internship, a Carnegie semester credit is worth 60 hours. Regarding the European equivalence, one ETCS (European Credit Transfer System) credit point corresponds to 30 hours of work. For clinical internships, an ETCS credit is equivalent to 45 hours. |
admission to the program

Admission criteria and prerequisites
Registration documents
Admission process
* Written tests (general knowledge, language proficiency and psychological assessment), and
* Personal interview with the candidate.
- High school diploma with a scientific specialization (Abitur, Bac, GCE-A Level)
- Fluency in the language of instruction (French or German or English)
- Computer skills
- Good morals
- Physical and psychological aptitude
Registration documents
- A letter of application addressed to the director of the college;
- The application form filled and signed by the student;
- Three certified copies of the student's National Identity Card (CIN);
- Three certified copies of the High School Diploma;
- Three certified copies of the transcripts of the high school;
- Medical certificate of physical and mental fitness
- Six photos
Admission process
- Admission to this program is based on selection.
- The selection process is under the responsibility of the admissions committee of the program.
- The admissions committee consists of the academic director, the deputy academic director, the head of the department and the head of the admissions office.
- Admission takes place in three stages:
* Written tests (general knowledge, language proficiency and psychological assessment), and
* Personal interview with the candidate.
PROFESSIONAL CAREER
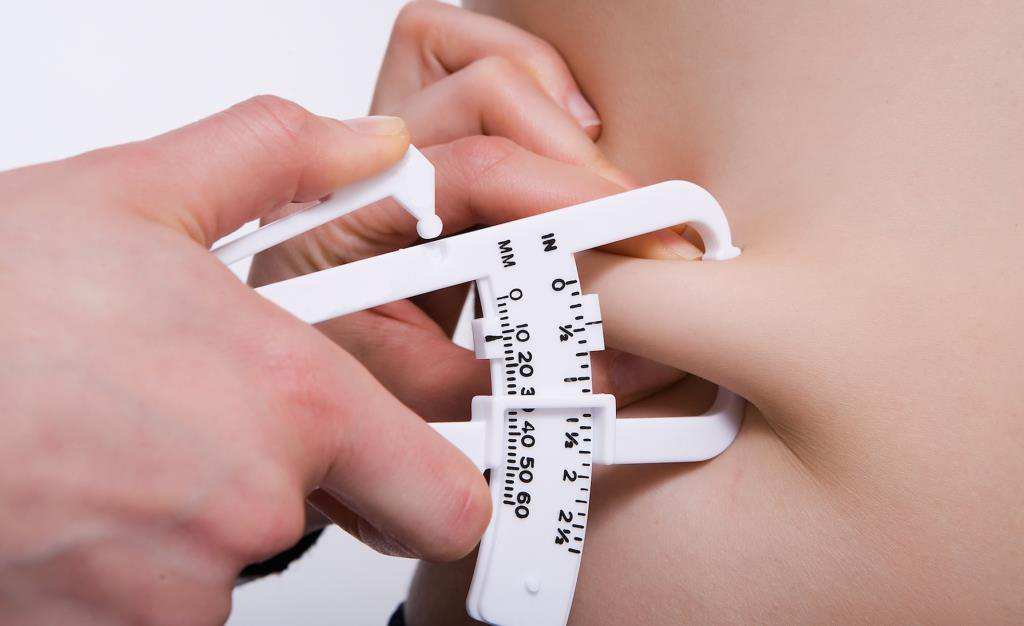
Dietitians work in clinical and community settings. In clinical institutions such as hospitals dietitians provide medical nutrition therapy for patients. They assess patients' nutritional needs, develop and implement nutrition programs, and evaluate and report the results. They confer with doctors and other healthcare professionals in order to coordinate medical and dietary needs. They also manage cases of overweight and contribute to treatment of critically-ill patients, such as those with renal disease and diabetes.
In community settings, dietitians develop nutrition programs designed to prevent disease and promote health, targeting particular groups of people. They work in public health clinics, fitness centers, wellness programs or home health agencies. Dieticians are also involved in food industry and management of food services in hotels, hostels, schools, hospitals and correction facilities
In community settings, dietitians develop nutrition programs designed to prevent disease and promote health, targeting particular groups of people. They work in public health clinics, fitness centers, wellness programs or home health agencies. Dieticians are also involved in food industry and management of food services in hotels, hostels, schools, hospitals and correction facilities
STRUCTURE OF THE ACADEMIC PROGRAM
FIRST SEMESTER
MODULE 01: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
US Semester credits: 4,0 | ECTS: 6,0 | Learning load: 180 Hours
Lectures: 45 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 90 Hours
US Semester credits: 4,0 | ECTS: 6,0 | Learning load: 180 Hours
Lectures: 45 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 90 Hours
MODULE 02: MIKROBIOLOGIE, HYGIENE UND INFEKTIONSKRANKHEITEN
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
MODULE 03: FOOD BIOCHEMISTRY
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
MODULE 04: DIGESTION AND METABOLISM
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
MODULE 05: FOOD MICROBIOLOGY
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
MODULE 06: FOOD TOXICOLOGY
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
MODULE 07: COMMUNICATION IN HEALTHCARE SETTINGS
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
SECOND SEMESTER
MODULE 08: PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
US Semester credits: 4,0 | ECTS: 6,0 | Learning load: 180 Hours
Lectures: 45 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 90 Hours
US Semester credits: 4,0 | ECTS: 6,0 | Learning load: 180 Hours
Lectures: 45 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 90 Hours
MODULE 09: NUTRITIONAL DISEASES
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
MODULE 10: INTRODUCTION TO NUTRITION
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
MODULE 11: CLINICAL AND NUTRITIONAL EXAMINATION
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
MODULE 12: FOOD SCIENCE
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
MODULE 13: SOCIAL AND HUMAN SCIENCES
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
MODULE 14: CLINICAL INTERNSHIP OF INITIATION
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 180 Hours
Supervised clinical learning activities: 180 Hours
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 180 Hours
Supervised clinical learning activities: 180 Hours
THIRD SEMESTER
MODULE 15: DIET AND DIETARY MODIFICATION
US Semester credits: 4,0 | ECTS: 6,0 | Learning load: 180 Hours
Lectures: 45 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 90 Hours
US Semester credits: 4,0 | ECTS: 6,0 | Learning load: 180 Hours
Lectures: 45 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 90 Hours
MODULE 16: NUTRITION DURING PREGNANCY AND LACTATION
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 45 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 90 Hours
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 45 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 90 Hours
MODULE 17: CHILD NUTRITION
US Semester credits: 4,0 | ECTS: 6,0 | Learning load: 180 Hours
Lectures: 45 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 90 Hours
US Semester credits: 4,0 | ECTS: 6,0 | Learning load: 180 Hours
Lectures: 45 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 90 Hours
MODULE 18: FOOD SAFETY AND HYGIENE
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
MODULE 19: RECHTLICHE UND ETHISCHE GRUNDLAGEN DER KRANKENPFLEGE
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
MODULE 20: CLINICAL PLACEMENTS OF PROFESSIONALIZATION 1
US Semester credits: 4,0 | ECTS: 6,0 | Learning load: 240 hours
Supervised clinical learning activities: 240 hours
US Semester credits: 4,0 | ECTS: 6,0 | Learning load: 240 hours
Supervised clinical learning activities: 240 hours
FOURTH SEMESTER
MODULE 21: NUTRITION AND CHRONIC DISEASES
US Semester credits: 4,0 | ECTS: 6,0 | Learning load: 180 Hours
Lectures: 45 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 90 Hours
US Semester credits: 4,0 | ECTS: 6,0 | Learning load: 180 Hours
Lectures: 45 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 90 Hours
MODULE 22: ARTIFICIAL NUTRITION
US Semester credits: 4,0 | ECTS: 6,0 | Learning load: 180 Hours
Lectures: 45 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 90 Hours
US Semester credits: 4,0 | ECTS: 6,0 | Learning load: 180 Hours
Lectures: 45 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 90 Hours
MODULE 23: GERIATRIC NUTRITION
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
MODULE 24: COOKING TECHNIQUES
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 90 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 90 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
MODULE 25: EPIDEMIOLOGY, BIOSTATISTICS AND RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
MODULE 26: CLINICAL PLACEMENTS OF PROFESSIONALIZATION 2
US Semester credits: 4,0 | ECTS: 6,0 | Learning load: 240 hours
Supervised clinical learning activities: 240 hours
US Semester credits: 4,0 | ECTS: 6,0 | Learning load: 240 hours
Supervised clinical learning activities: 240 hours
FIFTH SEMESTER
MODULE 27: CLINICAL NUTRITION 1
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
MODULE 28: SPORTS NUTRITION
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
MODULE 29: PUBLIC HEALTH
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
MODULE 30: SCIENTIFIC AND PROFESSIONAL WRITING
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
MODULE 31: CLINICAL INTERNSHIPS OF PROFESSIONAL AUTONOMY 1
US Semester credits: 6,0 | ECTS: 9,0 | Learning load: 360 hours
Supervised clinical learning activities: 360 hours
US Semester credits: 6,0 | ECTS: 9,0 | Learning load: 360 hours
Supervised clinical learning activities: 360 hours
MODULE 32: CLINICAL INTERNSHIPS OF PROFESSIONAL AUTONOMY 2
US Semester credits: 6,0 | ECTS: 9,0 | Learning load: 360 hours
Supervised clinical learning activities: 360 hours
US Semester credits: 6,0 | ECTS: 9,0 | Learning load: 360 hours
Supervised clinical learning activities: 360 hours
SIXTH SEMESTER
MODULE 33: CLINICAL NUTRITION 1 2
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
MODULE 34: PUBLIC HEALTH NUTRITION
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
MODULE 35: MANAGEMENT AND LEADERSHIP
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
MODULE 36: PROFESSIONAL AND INTERPERSONAL COMMUNICATION
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
MODULE 37-38: END-OF-STUDY INTERNSHIP AND PROJECT
US Semester credits: 12,0 | ECTS: 18,0 | Learning load: 720 Hours
Betreute klinische Lernaktivitäten: 720 Hours
US Semester credits: 12,0 | ECTS: 18,0 | Learning load: 720 Hours
Betreute klinische Lernaktivitäten: 720 Hours
SUMMARY DESCRIPTION OF THE MODULES
FIRST SEMESTER
MODULE 01: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
US Semester credits: 4,0 | ECTS: 6,0 | Learning load: 180 Hours
Lectures: 45 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 90 Hours
Lectures: 45 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 90 Hours
U01: The cell
U02: Tissues and skin
U03: The skeleton and muscles
U04: The nervous system
U05: The senses
U06: The endocrine system
U07: The blood and the lymphatic system
U08: The immune system
U09: The cardiovascular system
U10: The respiratory system
U11: The digestive system
U12: The urinary system
U13: Electrolyte and pH homeostasis
U14: The reproductive system
U15: Development and heritage
U02: Tissues and skin
U03: The skeleton and muscles
U04: The nervous system
U05: The senses
U06: The endocrine system
U07: The blood and the lymphatic system
U08: The immune system
U09: The cardiovascular system
U10: The respiratory system
U11: The digestive system
U12: The urinary system
U13: Electrolyte and pH homeostasis
U14: The reproductive system
U15: Development and heritage
MODULE 02: MIKROBen, HYGIENE UND INFEKTIONSKRANKHEITEN
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
Unit 01: General microbiology
Unit 02: Bacterial infections
Unit 03: Viral infections
Unit 04: Parasitic infestations
Unit 05: More Infections
Unit 06: Control of microbial infections
Unit 07: Prevention of infections
Unit 08: Vaccination
Unit 09: Sterilization and disinfection
Unit 10: Antibiotics and antiviral therapies
Unit 11: Antibiotic resistance
Unit 12: Nosocomial infections
Unit 13: Epidemics
Unit 14: Biotechnology
Unit 15: Bioterrorism
Unit 02: Bacterial infections
Unit 03: Viral infections
Unit 04: Parasitic infestations
Unit 05: More Infections
Unit 06: Control of microbial infections
Unit 07: Prevention of infections
Unit 08: Vaccination
Unit 09: Sterilization and disinfection
Unit 10: Antibiotics and antiviral therapies
Unit 11: Antibiotic resistance
Unit 12: Nosocomial infections
Unit 13: Epidemics
Unit 14: Biotechnology
Unit 15: Bioterrorism
MODULE 03: FOOD BIOCHEMISTRY
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
Unit 01: Carbohydrates
Unit 02: Lipids
Unit 03: Amino acids and proteins
Unit 04: Immunoglobins and enzymes
Unit 05: Intermolecular forces and connections
Unit 06: Importance of water in food
Unit 07: Vitamins and Minerals
Unit 08: Carbohydrate structures in food
Unit 09: Food proteins
Unit 10: Food Fats
Unit 11: Food additives
Unit 12: Oxidation of lipids
Unit 13: Non-enzymatic browning
Unit 14: Enzymatic Browning
Unit 02: Lipids
Unit 03: Amino acids and proteins
Unit 04: Immunoglobins and enzymes
Unit 05: Intermolecular forces and connections
Unit 06: Importance of water in food
Unit 07: Vitamins and Minerals
Unit 08: Carbohydrate structures in food
Unit 09: Food proteins
Unit 10: Food Fats
Unit 11: Food additives
Unit 12: Oxidation of lipids
Unit 13: Non-enzymatic browning
Unit 14: Enzymatic Browning
MODULE 04: DIGESTION AND METABOLISM
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
U01: Anatomy of the digestive system
U02: Digestive motility
U03: Digestive secretions
U04: Digestion and absorption
U05: Bioenergetics and cellular respiration
U06: Carbohydrate metabolism
U07: Lipid metabolism
U08: Metabolism of proteins and nucleic Acids
U02: Digestive motility
U03: Digestive secretions
U04: Digestion and absorption
U05: Bioenergetics and cellular respiration
U06: Carbohydrate metabolism
U07: Lipid metabolism
U08: Metabolism of proteins and nucleic Acids
MODULE 05: FOOD MICROBIOLOGY
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
Unit 01: Microorganisms in food
Unit 02: Food poisoning
Unit 03: Factors influencing food spoilage
Unit 04: Preservation of food
Unit 05: Microbiology of plant food
Unit 06: Production and desired modification of plant-based foods
Unit 07: Microbiology of animal food
Unit 08: Special foods
Unit 09: Industrial hygiene
Unit 02: Food poisoning
Unit 03: Factors influencing food spoilage
Unit 04: Preservation of food
Unit 05: Microbiology of plant food
Unit 06: Production and desired modification of plant-based foods
Unit 07: Microbiology of animal food
Unit 08: Special foods
Unit 09: Industrial hygiene
MODULE 06: FOOD TOXICOLOGY
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
Unit 01: Risk assessment in food toxicology
Unit 02: Microbial toxins
Unit 03: Algae toxins
Unit 04: Prions
Unit 05: Radionuclides
Unit 06: Heavy metals
Unit 07: Nitrate and nitrite
Unit 08: Organic contaminants
Unit 09: Acrylamide
Unit 10: Herbicides, fungicides, and insecticides
Unit 11: Veterinary medicinal products
Unit 12: Preservatives
Unit 13: Colors and sweeteners
Unit 14: Ethanol and biogenic amines
Unit 15: Toxic plant ingredients
Unit 16: Novel foods
Unit 02: Microbial toxins
Unit 03: Algae toxins
Unit 04: Prions
Unit 05: Radionuclides
Unit 06: Heavy metals
Unit 07: Nitrate and nitrite
Unit 08: Organic contaminants
Unit 09: Acrylamide
Unit 10: Herbicides, fungicides, and insecticides
Unit 11: Veterinary medicinal products
Unit 12: Preservatives
Unit 13: Colors and sweeteners
Unit 14: Ethanol and biogenic amines
Unit 15: Toxic plant ingredients
Unit 16: Novel foods
MODULE 07: COMMUNICATION IN HEALTHCARE SETTINGS
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
Unit 01: Welcoming a patient
Unit 02: Undertaking patient's care
Unit 03: Take the vital signs
Unit 04: Making a gesture of care
Unit 05: Educate the patient
Unit 06: Request a medical prescription
Unit 07: Written and oral reports
Unit 08: Organize for the patient discharge
Unit 09: Prepare for joining a team of care
Unit 10: Applying for a clinical placement/internship
Unit 02: Undertaking patient's care
Unit 03: Take the vital signs
Unit 04: Making a gesture of care
Unit 05: Educate the patient
Unit 06: Request a medical prescription
Unit 07: Written and oral reports
Unit 08: Organize for the patient discharge
Unit 09: Prepare for joining a team of care
Unit 10: Applying for a clinical placement/internship
SECOND SEMESTER
MODULE 08: PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
US Semester credits: 4,0 | ECTS: 6,0 | Learning load: 180 Hours
Lectures: 45 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 90 Hours
Lectures: 45 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 90 Hours
Unit 01: Basic concepts of pathophysiology
Unit 02: Immunity, inflammation, and hypersensitivity
Unit 03: Genes and genetic disorders
Unit 04: Cell proliferation and cancer
Unit 05: Diseases of the nervous system
Unit 06: Diseases of the sensory organs: eye and ear
Unit 07: Diseases of the endocrine system
Unit 08: Blood diseases
Unit 09: Diseases of the immune system
Unit 10: Diseases of the cardiovascular system
Unit 11: Diseases of the respiratory system
Unit 12: Diseases of the kidney and the draining urinary system
Unit 13: Disorders of water, electrolyte, and acid-base balance
Unit 14: Diseases of the sexual organs
Unit 15: Diseases of the digestive system
Unit 16: Diseases of the musculoskeletal system
Unit 17: Disorders of the skin, hair, and nails
Unit 02: Immunity, inflammation, and hypersensitivity
Unit 03: Genes and genetic disorders
Unit 04: Cell proliferation and cancer
Unit 05: Diseases of the nervous system
Unit 06: Diseases of the sensory organs: eye and ear
Unit 07: Diseases of the endocrine system
Unit 08: Blood diseases
Unit 09: Diseases of the immune system
Unit 10: Diseases of the cardiovascular system
Unit 11: Diseases of the respiratory system
Unit 12: Diseases of the kidney and the draining urinary system
Unit 13: Disorders of water, electrolyte, and acid-base balance
Unit 14: Diseases of the sexual organs
Unit 15: Diseases of the digestive system
Unit 16: Diseases of the musculoskeletal system
Unit 17: Disorders of the skin, hair, and nails
MODULE 09: NUTRITIONAL DISEASES
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
Unit 01: Malnutrition
Unit 02: Vitamin Deficiency
Unit 03: Eating Disorders
Unit 04: Metabolic Syndrome
Unit 05: Adult Obesity
Unit 06: Diabetes
Unit 07: Hyperuricemia and Gout
Unit 08: Alcohol, Excessive Alcoholism and Alcoholism
Unit 09: Food allergies
Unit 02: Vitamin Deficiency
Unit 03: Eating Disorders
Unit 04: Metabolic Syndrome
Unit 05: Adult Obesity
Unit 06: Diabetes
Unit 07: Hyperuricemia and Gout
Unit 08: Alcohol, Excessive Alcoholism and Alcoholism
Unit 09: Food allergies
MODULE 10: INTRODUCTION TO NUTRITION
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
Unit 01: Basics of nutrition
Unit 02: Dietary requirements and recommended dietary allowances
Unit 03: Food models
Unit 04: Nutritional diagnosis
Unit 05: Diet recipes
Unit 06: Nutritional therapy education
Unit 02: Dietary requirements and recommended dietary allowances
Unit 03: Food models
Unit 04: Nutritional diagnosis
Unit 05: Diet recipes
Unit 06: Nutritional therapy education
MODULE 11: CLINICAL AND NUTRITIONAL EXAMINATION
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
Unit 01: Observation of nutritional status
Unit 02: The nutrition assessment interview
Unit 03: The general condition and vital signs
Unit 04: Clinical signs of malnutrition
Unit 05: Anthropometric measurements
Unit 06: Examination of the head and neck
Unit 07: Examination of the glands
Unit 08: Examination of the skin
Unit 09: Examination of muscles and skeleton
Unit 10: Examination of the nervous system
Unit 11: Examination of internal organs
Unit 12: Examination of the digestive tract
Unit 13: Screening tools
Unit 14: Determination of body composition
Unit 15: Measuring muscle strength
Unit 16: parameters of muscle function
Unit 02: The nutrition assessment interview
Unit 03: The general condition and vital signs
Unit 04: Clinical signs of malnutrition
Unit 05: Anthropometric measurements
Unit 06: Examination of the head and neck
Unit 07: Examination of the glands
Unit 08: Examination of the skin
Unit 09: Examination of muscles and skeleton
Unit 10: Examination of the nervous system
Unit 11: Examination of internal organs
Unit 12: Examination of the digestive tract
Unit 13: Screening tools
Unit 14: Determination of body composition
Unit 15: Measuring muscle strength
Unit 16: parameters of muscle function
MODULE 12: FOOD SCIENCE
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
Unit 01: Diet selection and evaluation
Unit 02: Meat and poultry
Unit 03: Fish and crustaceans
Unit 04: Milk and cheese
Unit 05: Eggs
Unit 06: Vegetables and legumes
Unit 07: Fruit
Unit 08: Soups, salads, and gelatin
Unit 09: Grains and pasta
Unit 10: Loaves
Unit 11: Sweeteners
Unit 12: Fats and oils
Unit 13: Cake and cookies
Unit 14: Pastries and cakes
Unit 15: Sweets and icy desserts
Unit 16: water and drinks
Unit 02: Meat and poultry
Unit 03: Fish and crustaceans
Unit 04: Milk and cheese
Unit 05: Eggs
Unit 06: Vegetables and legumes
Unit 07: Fruit
Unit 08: Soups, salads, and gelatin
Unit 09: Grains and pasta
Unit 10: Loaves
Unit 11: Sweeteners
Unit 12: Fats and oils
Unit 13: Cake and cookies
Unit 14: Pastries and cakes
Unit 15: Sweets and icy desserts
Unit 16: water and drinks
MODULE 13: SOCIAL AND HUMAN SCIENCES
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
Unit 01: Major domains of psychology
Unit 02: Basic concepts in cognitive psychology
Unit 03: Basic concepts in clinical psychology
Unit 04: Development of the person and personality
Unit 05: Basic concepts in social psychology
Unit 06: Basic concepts of health psychology
Unit 07: Major fields of sociology
Unit 08: Basic concepts in sociology
Unit 09: Basic concepts in anthropology and ethnology
Unit 10: Caring relationship and its human aspects
Unit 11: Dynamics in caring relationships
Unit 02: Basic concepts in cognitive psychology
Unit 03: Basic concepts in clinical psychology
Unit 04: Development of the person and personality
Unit 05: Basic concepts in social psychology
Unit 06: Basic concepts of health psychology
Unit 07: Major fields of sociology
Unit 08: Basic concepts in sociology
Unit 09: Basic concepts in anthropology and ethnology
Unit 10: Caring relationship and its human aspects
Unit 11: Dynamics in caring relationships
MODULE 14: CLINICAL INTERNSHIP OF INITIATION
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 180 Hours
Supervised clinical learning activities: 180 Hours
Supervised clinical learning activities: 180 Hours
Rotations:
These rotations take place in one or more of the following facilities:
- Internship in internal medicine (60 hours)
- Internship in general surgery (60 hours)
- Introductory internship in dietetics and nutrition (60 hours)
These rotations take place in one or more of the following facilities:
- Casablanca Health Directorate Public Hospitals
- Ibn Rochd University Hospital of Casablanca
- Private hospitals in partnership with the School of Health Sciences with appropriate professional supervision.
THIRD SEMESTER
MODULE 15: DIET AND DIETARY MODIFICATION
US Semester credits: 4,0 | ECTS: 6,0 | Learning load: 180 Hours
Lectures: 45 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 90 Hours
Lectures: 45 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 90 Hours
Unit 01: Diet recipes that require a change in texture
Unit 02: Diet recipes that require a change in the recommended energy intake
Unit 03: Diet recipes that require a change in recommended protein intake
Unit 04: Diet recipes that require a change in the recommended lipid intake
Unit 05: Diet recipes that require a change in the recommended carbohydrate intake
Unit 06: Diet recipes that require a change in the recommended intake of fat and carbohydrates
Unit 07: Diet recipes that require a change in the recommended fat and carbohydrate intake
Unit 08: Diet recipes that require a change in the recommended mineral intake
Unit 09: Diet recipes that require a change in the recommended fiber intake
Unit 10: Diet recipes that require an overall qualitative change in the energy supply
Unit 02: Diet recipes that require a change in the recommended energy intake
Unit 03: Diet recipes that require a change in recommended protein intake
Unit 04: Diet recipes that require a change in the recommended lipid intake
Unit 05: Diet recipes that require a change in the recommended carbohydrate intake
Unit 06: Diet recipes that require a change in the recommended intake of fat and carbohydrates
Unit 07: Diet recipes that require a change in the recommended fat and carbohydrate intake
Unit 08: Diet recipes that require a change in the recommended mineral intake
Unit 09: Diet recipes that require a change in the recommended fiber intake
Unit 10: Diet recipes that require an overall qualitative change in the energy supply
MODULE 16: NUTRITION DURING PREGNANCY AND LACTATION
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
Unit 01: Nutritional and health needs during normal pregnancy
Unit 02: Nutritional recommendations and dietary guidelines for pregnant women
Unit 03: Optimal weight gain
Unit 04: Developing food, folklore, and taste preferences
Unit 05: Obesity and pregnancy
Unit 06: Nutrition in multifetal pregnancy
Unit 07: Eating disorders during pregnancy
Unit 08: Diabetes and pregnancy
Unit 09: Preeclampsia
Unit 10: Food supplements during pregnancy
Unit 11: Vegetarian nutrition during pregnancy
Unit 12: Iron and folic acid requirements and unwanted results
Unit 13: Nutritional recommendations and nutritional guidelines during the postpartum period
Unit 14: Nutritional problems while breastfeeding
Unit 15: Diet and postpartum depression
Unit 02: Nutritional recommendations and dietary guidelines for pregnant women
Unit 03: Optimal weight gain
Unit 04: Developing food, folklore, and taste preferences
Unit 05: Obesity and pregnancy
Unit 06: Nutrition in multifetal pregnancy
Unit 07: Eating disorders during pregnancy
Unit 08: Diabetes and pregnancy
Unit 09: Preeclampsia
Unit 10: Food supplements during pregnancy
Unit 11: Vegetarian nutrition during pregnancy
Unit 12: Iron and folic acid requirements and unwanted results
Unit 13: Nutritional recommendations and nutritional guidelines during the postpartum period
Unit 14: Nutritional problems while breastfeeding
Unit 15: Diet and postpartum depression
MODULE 17: CHILD NUTRITION
US Semester credits: 4,0 | ECTS: 6,0 | Learning load: 180 Hours
Lectures: 45 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 90 Hours
Lectures: 45 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 90 Hours
Unit 01: Nutrition of the normal newborns
Unit 01: Nutrition of premature newborns
Unit 03: Infant nutrition
Unit 04: The child and certain food contexts
Unit 05: Diet-related diseases in children
Unit 06: The child in a pathological situation
Unit 07: Nutritional status of the child
Unit 08: Nutritional measures
Unit 09: The Teenager
Unit 01: Nutrition of premature newborns
Unit 03: Infant nutrition
Unit 04: The child and certain food contexts
Unit 05: Diet-related diseases in children
Unit 06: The child in a pathological situation
Unit 07: Nutritional status of the child
Unit 08: Nutritional measures
Unit 09: The Teenager
MODULE 18: FOOD SAFETY AND HYGIENE
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
U01: Regulatory overview
U02: Hazards and Risks
U03: The HACCP Method
U04: Microorganisms
U05: Premises and equipment
U06: Hygiene and safety of personnel
U07: Cleaning, hygiene, and disinfection
U08: Good Hygiene Practices (BPH)
U09: Management of non-conformity
U10: Traceability
U11: Crisis Management
U02: Hazards and Risks
U03: The HACCP Method
U04: Microorganisms
U05: Premises and equipment
U06: Hygiene and safety of personnel
U07: Cleaning, hygiene, and disinfection
U08: Good Hygiene Practices (BPH)
U09: Management of non-conformity
U10: Traceability
U11: Crisis Management
MODULE 19: RECHTLICHE UND ETHISCHE GRUNDLAGEN DER KRANKENPFLEGE
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
Unit 01: Basic concepts in healthcare ethics
Unit 02: Professional practice and responsibility
Unit 03: Human rights
Unit 04: Patients' rights
Unit 05: Confidentiality and professional secrecy
Unit 06: Principles of law for healthcare professionals
Unit 07: Concepts of responsibility
Unit 02: Professional practice and responsibility
Unit 03: Human rights
Unit 04: Patients' rights
Unit 05: Confidentiality and professional secrecy
Unit 06: Principles of law for healthcare professionals
Unit 07: Concepts of responsibility
MODULE 20: CLINICAL PLACEMENTS OF PROFESSIONALIZATION 1
US Semester credits: 4,0 | ECTS: 6,0 | Learning load: 240 hours
Supervised clinical learning activities: 240 hours
Supervised clinical learning activities: 240 hours
Rotations:
These rotations take place in one or more of the following facilities:
- Clinical Dietetics Internship - Hospital Dietetics Department (80 hours)
- Internship in Maternal Nutrition - Obstetrics Department (80 hours)
- Internship in Pediatric Nutrition - Department of Pediatrics (80 hours)
These rotations take place in one or more of the following facilities:
- Casablanca Health Directorate Public Hospitals
- Ibn Rochd University Hospital of Casablanca
- Private hospitals in partnership with the School of Health Sciences with appropriate professional supervision.
FOURTH SEMESTER
MODULE 21: NUTRITION AND CHRONIC DISEASES
US Semester credits: 4,0 | ECTS: 6,0 | Learning load: 180 Hours
Lectures: 45 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 90 Hours
Lectures: 45 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 90 Hours
U01: Cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, dyslipidemia
U02: Nutrition and digestive pathologies
U03: Hepatobiliary and pancreatic diseases
U04: Nutrition and infection
U05: Nutrition and renal pathology in adults
U06: Nutrition and cancer
U07: Food and osteoarticular apparatus
U08: Diseases of metabolism
U09: Respiratory diseases
U10: Nutrition and neurological conditions
U02: Nutrition and digestive pathologies
U03: Hepatobiliary and pancreatic diseases
U04: Nutrition and infection
U05: Nutrition and renal pathology in adults
U06: Nutrition and cancer
U07: Food and osteoarticular apparatus
U08: Diseases of metabolism
U09: Respiratory diseases
U10: Nutrition and neurological conditions
MODULE 22: Artificial nutrition
US Semester credits: 4,0 | ECTS: 6,0 | Learning load: 180 Hours
Lectures: 45 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 90 Hours
Lectures: 45 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 90 Hours
Unit 01: Introduction to Artificial Nutrition
Unit 02: Enteral Nutrition
Unit 03: Parenteral Nutrition
Unit 04: Ambulatory enteral and parenteral nutrition
Unit 05: Nutrition of the critically ill in the intensive care unit
Unit 06: Artificial feeding practice
Unit 02: Enteral Nutrition
Unit 03: Parenteral Nutrition
Unit 04: Ambulatory enteral and parenteral nutrition
Unit 05: Nutrition of the critically ill in the intensive care unit
Unit 06: Artificial feeding practice
MODULE 23: Geriatric nutrition
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
Lectures: 30 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 60 Hours
Unit 01: Introduction to gerontology
Unit 02: Normal changes in aging
Unit 03: Assessing the elderly and care environments
Unit 04: Diseases of geriatrics
Unit 05: Nutritional needs of the elderly
Unit 06: Assessment of nutritional status
Unit 07: Anorexia and malnutrition
Unit 08: Nutrition of elderly patients with metabolic aggression
Unit 09: Nutrition and hydration at the end of life
Unit 02: Normal changes in aging
Unit 03: Assessing the elderly and care environments
Unit 04: Diseases of geriatrics
Unit 05: Nutritional needs of the elderly
Unit 06: Assessment of nutritional status
Unit 07: Anorexia and malnutrition
Unit 08: Nutrition of elderly patients with metabolic aggression
Unit 09: Nutrition and hydration at the end of life
MODULE 24: COOKING TECHNIQUES
US Semester credits: 3,0 | ECTS: 4,5 | Learning load: 135 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 90 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 90 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
Unit 01: Kitchen equipment and appliance
Unit 02: Cooking utensils and instruments
Unit 03: Rational use of benevolence
Unit 04: Adaptations of culinary techniques to equipment and food
Unit 05: Different cooking modes
Unit 06: Various compounds and emulsions
Unit 07: Different types of pasta
Unit 08: Pranks
Unit 09: Spices, flavorings, herbs, and other spices
Unit 10: Feeding with modified texture
Unit 11: Diets
Unit 02: Cooking utensils and instruments
Unit 03: Rational use of benevolence
Unit 04: Adaptations of culinary techniques to equipment and food
Unit 05: Different cooking modes
Unit 06: Various compounds and emulsions
Unit 07: Different types of pasta
Unit 08: Pranks
Unit 09: Spices, flavorings, herbs, and other spices
Unit 10: Feeding with modified texture
Unit 11: Diets
MODULE 25: EPIDEMIOLOGY, BIOSTATISTICS AND RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
Unit 01: What is epidemiology?
Unit 02: Measures of health and disease
Unit 03: Types of studies
Unit 04: Introduction to biostatistics: Concepts and Instruments
Unit 05: Causality in epidemiology
Unit 06: Epidemiology and prevention of noncommunicable diseases
Unit 07: Communicable diseases: Epidemiology, surveillance, and action
Unit 08: The conceptual phase of research
Unit 09: The methodological phase of research
Unit 10: The empirical and analytical phase of research
Unit 11: The diffusion phase of research
Unit 02: Measures of health and disease
Unit 03: Types of studies
Unit 04: Introduction to biostatistics: Concepts and Instruments
Unit 05: Causality in epidemiology
Unit 06: Epidemiology and prevention of noncommunicable diseases
Unit 07: Communicable diseases: Epidemiology, surveillance, and action
Unit 08: The conceptual phase of research
Unit 09: The methodological phase of research
Unit 10: The empirical and analytical phase of research
Unit 11: The diffusion phase of research
MODULE 26: CLINICAL PLACEMENTS OF PROFESSIONALIZATION 2
US Semester credits: 4,0 | ECTS: 6,0 | Learning load: 240 hours
Supervised clinical learning activities: 240 hours
Supervised clinical learning activities: 240 hours
Rotations:
These rotations take place in one or more of the following facilities:
- Clinical Dietetics Internship - Hospital Dietetics Department (80 hours)
- Internship in geriatric nutrition - geriatric department or nursing home (80 hours)
- Internship in Sports Nutrition - Sports Medicine Department or Sports Club or Sports Rehabilitation Center or Fitness Studio (80 hours)
These rotations take place in one or more of the following facilities:
- Casablanca Health Directorate Public Hospitals
- Ibn Rochd University Hospital of Casablanca
- Private hospitals in partnership with the School of Health Sciences with appropriate professional supervision.
FIFTH SEMESTER
MODULE 27: CLINICAL NUTRITION 1
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
Case 01: Vegetarianism
Case 02: Nutritional screening
Case 03: Artificial nutrition in intensive care
Case 04: Eating Disorders
Case P05: Diet-treated obesity
Case 06: Obesity treated by surgery
Case 07: Gastritis in an elderly woman
Case 08: Chest pain in an elderly woman
Case 09: Pediatric gastro-esophageal reflux
Case 10: Inherited disorders of metabolism
Case 11: Peptic ulcer resulting from gastrectomy
Case 12: Diet and diverticulosis
Case 13: Cystic fibrosis
Case 14: Dietary management of atherosclerosis
Case 02: Nutritional screening
Case 03: Artificial nutrition in intensive care
Case 04: Eating Disorders
Case P05: Diet-treated obesity
Case 06: Obesity treated by surgery
Case 07: Gastritis in an elderly woman
Case 08: Chest pain in an elderly woman
Case 09: Pediatric gastro-esophageal reflux
Case 10: Inherited disorders of metabolism
Case 11: Peptic ulcer resulting from gastrectomy
Case 12: Diet and diverticulosis
Case 13: Cystic fibrosis
Case 14: Dietary management of atherosclerosis
MODULE 28: Sports nutrition
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
Unit 01: Energy requirements in athletes
Unit 02: Carbohydrate diet and muscle exercise
Unit 03: Fat and exercise
Unit 04: Protein intake and exercise
Unit 05: hydration and exercise
Unit 06: Mineral, vitamins, trace elements and sport
Unit 07: Oxidative stress and micronutrient antioxidant
Unit 08: Calcium ration and physical activity
Unit 09: Athlete's anemia and its treatment
Unit 10: Ergogenic nutritional aids and physical activity
Unit 11: Nutrition under special conditions
Unit 02: Carbohydrate diet and muscle exercise
Unit 03: Fat and exercise
Unit 04: Protein intake and exercise
Unit 05: hydration and exercise
Unit 06: Mineral, vitamins, trace elements and sport
Unit 07: Oxidative stress and micronutrient antioxidant
Unit 08: Calcium ration and physical activity
Unit 09: Athlete's anemia and its treatment
Unit 10: Ergogenic nutritional aids and physical activity
Unit 11: Nutrition under special conditions
MODULE 29: PUBLIC HEALTH
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
Unit 01: History of public health
Unit 02: Essential knowledge and skills in community health
Unit 03: Cross-cultural health
Unit 04: Health promotion
Unit 05: Public nutrition
Unit 06: Epidemiological concepts
Unit 07: Prevention of infectious diseases
Unit 08: Chronic diseases
Unit 09: The community approach to mental health
Unit 10: Environmental health
Unit 12: The development of community health programs
Unit 13: Health education
Unit 14: Social marketing
Unit 15: Health policy
Unit 02: Essential knowledge and skills in community health
Unit 03: Cross-cultural health
Unit 04: Health promotion
Unit 05: Public nutrition
Unit 06: Epidemiological concepts
Unit 07: Prevention of infectious diseases
Unit 08: Chronic diseases
Unit 09: The community approach to mental health
Unit 10: Environmental health
Unit 12: The development of community health programs
Unit 13: Health education
Unit 14: Social marketing
Unit 15: Health policy
MODULE 30: SCIENTIFIC AND PROFESSIONAL WRITING
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
Unit 01: Require less reader memory
Unit 02: Keeping the reader attentive
Unit 03: Reduce reading time
Unit 04: Keep the reader motivated
Unit 05: Bridging the knowledge gap
Unit 06: Creating expectations
Unit 07: Plotting a progression for smooth playback
Unit 08: Propel reading
Unit 09: Controlling energy expenditure
Unit 10: The title: a face
Unit 11: The summary: the heart
Unit 12: Titles and subtitles: a skeleton
Unit 13: The introduction: a hand
Unit 14: Introduction - traps
Unit 15: The visual element: a voice
Unit 16: The conclusion: a smile
Unit 02: Keeping the reader attentive
Unit 03: Reduce reading time
Unit 04: Keep the reader motivated
Unit 05: Bridging the knowledge gap
Unit 06: Creating expectations
Unit 07: Plotting a progression for smooth playback
Unit 08: Propel reading
Unit 09: Controlling energy expenditure
Unit 10: The title: a face
Unit 11: The summary: the heart
Unit 12: Titles and subtitles: a skeleton
Unit 13: The introduction: a hand
Unit 14: Introduction - traps
Unit 15: The visual element: a voice
Unit 16: The conclusion: a smile
MODULE 31: CLINICAL INTERNSHIPS OF PROFESSIONAL AUTONOMY 1
US Semester credits: 6,0 | ECTS: 9,0 | Learning load: 360 hours
Supervised clinical learning activities: 360 hours
Supervised clinical learning activities: 360 hours
Rotations:
These rotations take place in one or more of the following facilities:
- Internship in artificial nutrition (intensive care unit) (85 hours)
- Clinical Nutrition Internship (Department of Endocrinology and Metabolic Diseases) (85 hours)
- Internship in communal catering companies (85 hours)
- Internship in Hygiene Control of Food Establishments - Department of Public Health of the City of Casablanca (85 hours)
These rotations take place in one or more of the following facilities:
- Casablanca Health Directorate Public Hospitals
- Ibn Rochd University Hospital of Casablanca
- Private hospitals in partnership with the School of Health Sciences with appropriate professional supervision.
MODULE 32: CLINICAL INTERNSHIPS OF PROFESSIONAL AUTONOMY 2
US Semester credits: 6,0 | ECTS: 9,0 | Learning load: 360 hours
Supervised clinical learning activities: 360 hours
Supervised clinical learning activities: 360 hours
Rotations:
These rotations take place in one or more of the following facilities:
- Internship in Perioperative Nutrition - Surgical (85 hours)
- Internship in nutrition of critically ill patients (intensive care unit) (85 hours)
- Internship in a private practice for (85 hours)
- Internship in nutrition education and nutrition counseling - Health Department of the Casablanca-Settat region (85 hours)
These rotations take place in one or more of the following facilities:
- Health Department of the Casablanca-Settat Region
- Casablanca Health Directorate Public Hospitals
- Ibn Rochd University Hospital of Casablanca
- Private hospitals in partnership with the School of Health Sciences with appropriate professional supervision.
SIXTH SEMESTER
MODULE 33: CLINICAL NUTRITION 2
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
Unit 01: Myocardial infarction resulting in congestive heart failure
Unit 02: Diabetes mellitus type 1
Unit 03: Diabetes mellitus type 2 and metabolic syndrome
Unit 04: Complications of diabetes
Unit 05: Gestational Diabetes
Unit 06: Malnutrition and dehydration in old age
Unit 07: Esophageal cancer and chemotherapy
Unit 08: Colon cancer and malnutrition
Unit 09: Peritoneal Dialysis
Unit 10: Hypertension and diet
Unit 11: Hemodialysis and diet
Unit 12: Crohn's disease
Unit 13: Childhood obesity
Unit 14: Interactions medicinal plants
Unit 02: Diabetes mellitus type 1
Unit 03: Diabetes mellitus type 2 and metabolic syndrome
Unit 04: Complications of diabetes
Unit 05: Gestational Diabetes
Unit 06: Malnutrition and dehydration in old age
Unit 07: Esophageal cancer and chemotherapy
Unit 08: Colon cancer and malnutrition
Unit 09: Peritoneal Dialysis
Unit 10: Hypertension and diet
Unit 11: Hemodialysis and diet
Unit 12: Crohn's disease
Unit 13: Childhood obesity
Unit 14: Interactions medicinal plants
MODULE 34: PUBLIC HEALTH NUTRITION
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
Unit 01: Overview of public health nutrition
Unit 02: Nutritional epidemiology
Unit 03: Assessment of nutritional status in individuals and populations
Unit 04: Public health nutrition strategies and dietary guidelines
Unit 05: Food choice and preferences
Unit 06: Public health aspects of overnutrition
Unit 07: Public health aspects of undernutrition
Unit 08: Public health aspects of vitamin a deficiency
Unit 09: Public health aspects of iodine and iodine-deficiency disorders
Unit 10: Public health aspects of iron-deficiency anemias
Unit 11: Nutrition and adverse outcomes in pregnancy
Unit 12: Nutrition and cardiovascular disease
Unit 13: Nutrition and diabetes mellitus
Unit 14: Nutrition and cancer
Unit 15: Nutrition, osteoporosis, and hip fracture
Unit 02: Nutritional epidemiology
Unit 03: Assessment of nutritional status in individuals and populations
Unit 04: Public health nutrition strategies and dietary guidelines
Unit 05: Food choice and preferences
Unit 06: Public health aspects of overnutrition
Unit 07: Public health aspects of undernutrition
Unit 08: Public health aspects of vitamin a deficiency
Unit 09: Public health aspects of iodine and iodine-deficiency disorders
Unit 10: Public health aspects of iron-deficiency anemias
Unit 11: Nutrition and adverse outcomes in pregnancy
Unit 12: Nutrition and cardiovascular disease
Unit 13: Nutrition and diabetes mellitus
Unit 14: Nutrition and cancer
Unit 15: Nutrition, osteoporosis, and hip fracture
MODULE 35: MANAGEMENT AND LEADERSHIP
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
Unit 01: Basic concepts in management
Unit 02: Decision making
Unit 03: Change and conflicts
Unit 04: Delegation
Unit 05: Effective staffing
Unit 06: Budgeting
Unit 07: Planning
Unit 08: Time management
Unit 09: Quality Improvement
Unit 10: Legal and ethical aspects of health care
Unit 11: Preparation for first employment
Unit 02: Decision making
Unit 03: Change and conflicts
Unit 04: Delegation
Unit 05: Effective staffing
Unit 06: Budgeting
Unit 07: Planning
Unit 08: Time management
Unit 09: Quality Improvement
Unit 10: Legal and ethical aspects of health care
Unit 11: Preparation for first employment
MODULE 36: PROFESSIONAL AND INTERPERSONAL COMMUNICATION
US Semester credits: 2,0 | ECTS: 3,0 | Learning load: 90 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
Lectures: 15 Hours | Practical tutorials 45 Hours | Self-directed learning 30 Hours
Unit 01: Introduction to interpersonal communication
Unit 02: Communication models
Unit 03: Communication in management practice
Unit 04: Nonverbal communication and body language
Unit 05: Communication and patient safety: understanding the relationship
Unit 06: The transformational model of communication
Unit 07: Creating common meaning to achieve transformational outcomes
Unit 08: Introduction to caregiver-patient relationships
Unit 09: Factors affecting communication climates
Unit 10: Caregiver-patient relationships during grief and bereavement
Unit 11: Risk factors of health care communication
Unit 12: The team and communication strategies
Unit 02: Communication models
Unit 03: Communication in management practice
Unit 04: Nonverbal communication and body language
Unit 05: Communication and patient safety: understanding the relationship
Unit 06: The transformational model of communication
Unit 07: Creating common meaning to achieve transformational outcomes
Unit 08: Introduction to caregiver-patient relationships
Unit 09: Factors affecting communication climates
Unit 10: Caregiver-patient relationships during grief and bereavement
Unit 11: Risk factors of health care communication
Unit 12: The team and communication strategies
MODULE 37-38: END-OF-STUDY INTERNSHIP AND PROJECT
US Semester credits: 12,0 | ECTS: 18,0 | Learning load: 720 Hours
Betreute klinische Lernaktivitäten: 720 Hours
Betreute klinische Lernaktivitäten: 720 Hours
This end-of-study internship is compulsory during the sixth semester. The objective of this final internship is to consolidate the clinical competencies, achieve professional autonomy and prepare the student for real professional life.
During this internship, the student is required to select a research topic of relevance to the institution or the profession and achieve an independent research satisfying the requirements set by the College of Health Sciences. The supervision of such research is the mutual responsibility of the College and the hosting institution.
At the end of the internship, the student has to present and defend his research in front of a jury that evaluates the project and give it a note.
This internship is undertaken in a hospital environment in the following structures:
To ensure an enriching internship experience, the policy of the College of Health Sciences recommends that the entire duration of the internship be spent in a single institution devoted to the clinical domains of the specialty.
During this internship, the student is required to select a research topic of relevance to the institution or the profession and achieve an independent research satisfying the requirements set by the College of Health Sciences. The supervision of such research is the mutual responsibility of the College and the hosting institution.
At the end of the internship, the student has to present and defend his research in front of a jury that evaluates the project and give it a note.
This internship is undertaken in a hospital environment in the following structures:
- Centers of nutrition and dietetics affiliated to the Casablanca Health Department
- Departments of dietetics in public hospitals affiliated to the Casablanca Health Department that enjoy adequate professional supervision.
- University Hospital Ibn Rochd
- Partner hospitals in Europe that enjoy adequate professional supervision.
To ensure an enriching internship experience, the policy of the College of Health Sciences recommends that the entire duration of the internship be spent in a single institution devoted to the clinical domains of the specialty.
COLLEGE OF HEALTH SCIENCESAuthorized by the Ministry of Higher Education, Scientific Research and Professional Training (Authorization No. 434/2015)
Member of the Association of Schools of Public Health in the European Region (ASPHER) Partner of the City University of New York (CUNY) 14, Boulevard de Paris, 20000 Casablanca, Morocco Tel.: 0522475775 | Fax: 0522 475778 | Email: info@esss.ac.ma |

